Chain Abstraction
💡 Chain Abstraction is currently in experimental phase.
Chain Abstraction in WalletKit enables users with stablecoins on any network to spend them on-the-fly on a different network. Our Chain Abstraction solution provides a toolkit for wallet developers to integrate this complex functionality using WalletKit.
For example, when an app requests a 100 USDC payment on Base network but the user only has USDC on Arbitrum, WalletKit offers methods to detect this mismatch, generate necessary transactions, track the cross-chain transfer, and complete the original transaction after bridging finishes.
How It Works
Apps need to pass gas as null when sending a transaction to allow proper gas estimation by the wallet. Refer to this guide for more details.
When sending a transaction, you need to:
- Check if the required chain has enough funds to complete the transaction
- If not, use the
prepareDetailedmethod to generate necessary bridging transactions - Sign routing and initial transaction hashes, prepared by the prepare method
- Use
executemethod to broadcast routing and initial transactions and wait for it to be completed
The following sequence diagram illustrates the complete flow of a chain abstraction operation, from the initial dapp request to the final transaction confirmation
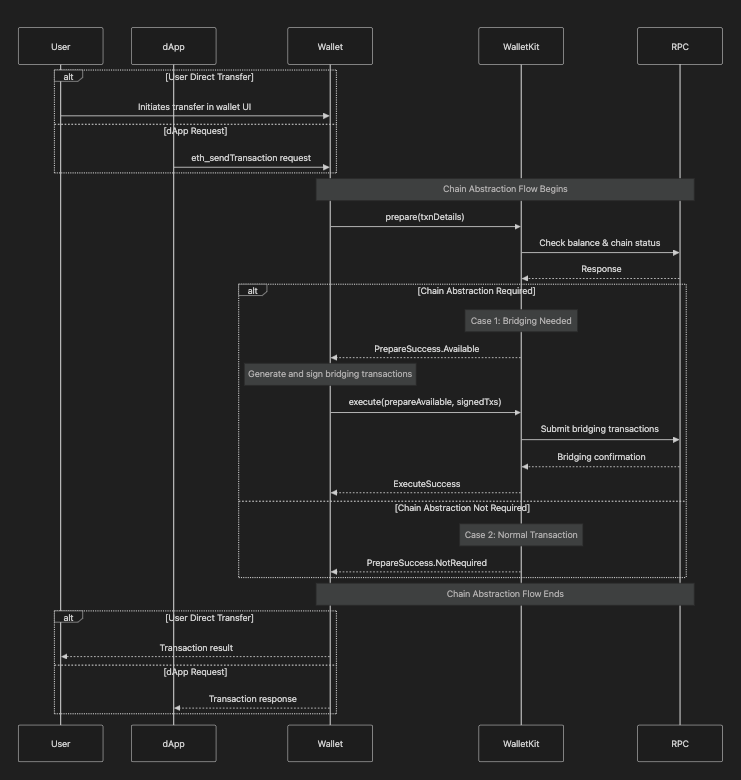
Methods
Make sure you are using canary version of @reown/walletkit.
Following are the methods from WalletKit that you will use in implementing chain abstraction.
Prepare
This method checks if a transaction requires additional bridging transactions beforehand.
public abstract prepareDetailed(params: {
transaction: ChainAbstractionTypes.PartialTransaction;
}): ChainAbstractionTypes.PrepareDetailedResponse;
Execute
Helper method used to broadcast the bridging and initial transactions and wait for them to be completed.
public abstract execute(params: {
orchestrationId: ChainAbstractionTypes.OrchestrationId;
bridgeSignedTransactions: ChainAbstractionTypes.SignedTransaction[];
initialSignedTransaction: ChainAbstractionTypes.SignedTransaction;
}): ChainAbstractionTypes.ExecuteResult;
Usage
When sending a transaction, first check if chain abstraction is needed using the prepareDetailed method.
If it is needed, you must sign all the fulfillment transactions and use the execute method.
Here's a complete example:
// Check if chain abstraction is needed
const result = await walletKit.chainAbstraction.prepareDetailed({
transaction: {
from: transaction.from as `0x${string}`,
to: transaction.to as `0x${string}`,
// @ts-ignore - cater for both input or data
input: transaction.input || (transaction.data as `0x${string}`),
chainId: chainId,
},
});
// Handle the prepare result
if ('success' in result) {
if ('notRequired' in result.success) {
// No bridging required, proceed with normal transaction
console.log('no routing required');
} else if ('available' in result.success) {
const available = result.success.available;
// Sign all bridge transactions and initial transaction
const bridgeTxs = available.route.map(tx => tx.transactionHashToSign);
const signedBridgeTxs = bridgeTxs.map(tx => wallet.signAny(tx));
const signedInitialTx = wallet.signAny(available.initial.transactionHashToSign);
// Execute the chain abstraction
const result = await walletKit.chainAbstraction.execute({
bridgeSignedTransactions: signedBridgeTxs,
initialSignedTransaction: signedInitialTx,
orchestrationId: available.routeResponse.orchestrationId,
});
}
}
For example, check out implementation of chain abstraction in sample wallet built with React.
Testing
To test Chain Abstraction, you can use the AppKit laboratory and try sending USDC/USDT with any chain abstraction supported wallet. You can also use this sample wallet for testing.